

| ArcFM Desktop > Geodatabase Replication Overview |
 |
Geodatabase Replication at version 10.0.1 and later requires that the ArcGIS table structure be version 10. If the ArcGIS table structure is version 9, Geodatabase Replication 10.0.1 and later will experience errors. |
Geodatabase Replication allows you to quickly synchronize a client geodatabase -- either personal (.mdb) or file (.gdb) -- with the most recent version of an SDE geodatabase.
One application of this functionality is for Mobile Solution users. Geodatabase Replication may be used by a field user to connect to the enterprise and update his field geodatabase with the most recent edits to a specified version (generally SDE.Default) in the SDE geodatabase. This version – called the sync version – is specified in a configuration file. This tool may be used by any application that requires a field geodatabase to be synchronized with the SDE geodatabase.
 |
The Geodatabase Replication Administrator tool requires that the user have Administrator privileges. |
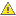
Geodatabase Replication (GDB Replication) consists of three components: Replication Server, Web Service and Client.
The image below depicts the Geodatabase Replication components and how they interact. The Replication Server and Web Service may reside on the same server or different servers. You may also have multiple replication servers retrieving data from a variety of SDE geodatabases and multiple web services providing the client with delta files.
The Base Path is the location in which the Replication Server places personal geodatabase (.mdb) or file geodatabase (.gdb) files that have been extracted from the SDE geodatabase. The Web Service accesses the Base Path and compares the client and server geodatabases to create a delta file, which it provides to the client. The Base Path may reside in any number of places (e.g., Replication Server, Web Server). Its location is specified in the server configuration file.
Figure 1, Process Flow
Replication consists of two separate processes. In the first process (A) the Replication Server extracts a replica of the initial extract version (e.g., SDE.Default) in the SDE geodatabase and places the extracted geodatabase (personal or file) at the Base Path.
Each extracted geodatabase is stored in a separate folder in the Base Path directory (e.g., ServerBase). The Server only stores the last update received before the current request. So, when the current request is filled, there are two versions of the SDE geodatabase in the Base Path: the most recent request and the last request before it.
In the example below, only the last Extract folder contains a geodatabase (Extract_2006_06-26-08-50-37), which is used to compare with the sync version and create a delta. All other Extract folders should contain one .hash and one .sig file (personal geodatabases), or one .hash and one .uid (file geodatabases). This directory may also contain .delta.zip and .xml files as well (if you have configured to save these files). Do not open or modify any geodatabase in these directories.
Should something occur to modify one of the databases in the Base Path directory, replication will fail. If this happens you will need to reinitialize Geodatabase Replication.
Figure 2, Base Path Directory Structure
In the second process (B), the Web Service provides the Client with updates from the Base Path. The Web Service receives the request from the Client and compares the identifiers of the client geodatabase with the identifiers stored in the extract folders in the Server Base Path to create a delta file. This delta file contains all changes between the client's last replication update and the most recent geodatabase stored in the Server Base Path. Once the delta has been created, the older of the two geodatabases is removed from the Base Path, and the most recent extract is retained. The Web Service passes the delta file to the GDB Replication Client. The Client uses this delta to update the geodatabase.
While the example focuses on updating a field database for use with the Mobile Solution, Geodatabase Replication may be used to synchronize a geodatabase with the SDE geodatabase for any number of applications.
The following sections describe how to configure the various components of Geodatabase Replication for use.
The following sections describe how to maintain your replicas and replica schemas.