

Version: 10.2.1c and 10.2.1c SP3 |
| Responder Overview > Troubleshooting > MSMQ Troubleshooting > Diagnosing MSMQ Problems |
Ensure your client and server machines have the exact same Message Queuing configuration. Select the exact same Message Queue sub-components. If the server only has “Common” installed then the client must also only have “Common”.
Responder uses only private queues and therefore requires only the “Common” MSMQ components. Public queues are not used and therefore Active Directory sub-components are not necessary.
The following registry key (for development purposes only) overrides the information specified in the remoting configuration: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Miner and Miner\Responder8\Channels\MSMQ\Client. Make sure the ComputerName attribute is specified correctly. See Configuring Responder for more information.
Verify that the client machine can access the destination (server) machine. The best way to do this is to open a command prompt and start a telnet session:
telnet <machine|ip> 1801
Note: You can install Telnet from the Microsoft website.
The communication between client and server engages many queues. View the outgoing queues to determine where the communication is incorrect. Since two-way communication includes timeouts, do this immediately after opening Responder Explorer (within the timeout period).
This diagram displays the message queues that participate in our custom MSMQ remoting channel implementation. It is helpful to understand this when diagnosing problems - particularly when looking at the outgoing queues.
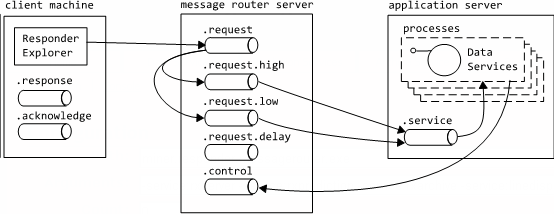
If you experience a reach queue error, such as "The queue does not exist or you do not have sufficient permissions to perform the operation", or a message indicates a queue could have been deleted, you can try removing the queues prior to contacting support.
By removing queues, Responder has the opportunity to erase any current issues and start again. To remove queues: