CIM provides a detailed model the equipment in an electric network. Note that this model will vary somewhat based on the version of CIM and adjustments for a specific implementation profile. The equipment model in NA reflects the foundational entities and relatationships in CIM. However, the actual equipment entities and relationships appearing in an exported feeder depend on the content of the mapping XML.
To support this equipment model, the Core CIM model in NA includes the objects described in this section.
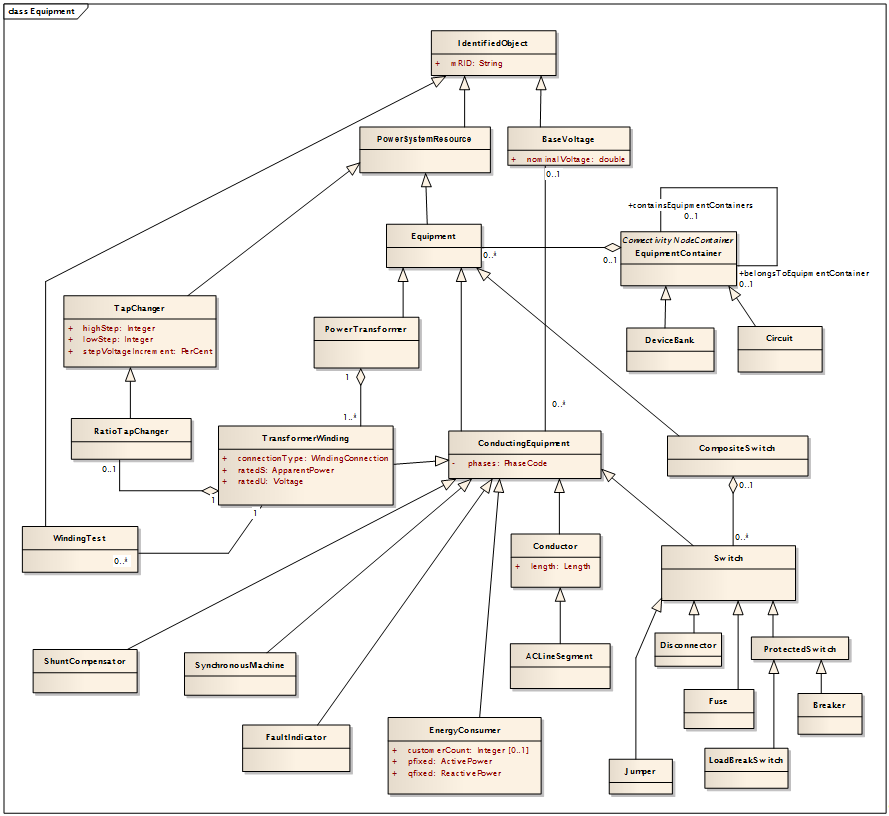
- IdentifiedObject: The root class containing the unique master resource ID.
- PowerSystemResource: A power system resource can be an item of equipment such as a Switch, an EquipmentContainer containing many individual items of equipment such as a Substation. A power system resource can have a location.
- BaseVoltage: A nominal base voltage which is referenced in the system.
- Equipment: The parts of a power system that are physical devices, electronic or mechanical.
- Equipment Container: A modeling construct to provide a root class for containing equipment.
- DeviceBank: DeviceBank is simply series and/or parallel combination of components that are usually identical.
- Circuit: An equipment container that will typically include conductors, energy consumers, transformers and transformer windings, switches, shunt compensators, etc., likely at different voltages. Circuit extends from a substation to a set of open points (radial circuit), or to a second substation (looped circuit).
- CompositeSwitch: A model of a set of individual Switches normally enclosed within the same cabinet and possibly with interlocks that restrict the combination of switch positions.
- Switch: A generic device designed to close, or open, or both, one or more electric circuits.
- ProtectedSwitch: A Switch that can be operated by protection equipment.
- Breaker: A ProtectedSwitch capable of making, carrying, and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time, and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions, e.g. those of short circuit.
- LoadBreakSwitch: A ProtectedSwitch capable of making, carrying, and breaking currents under normal operating conditions.
- Fuse: An overcurrent protective device with a circuit opening fusible part that is heated and severed by the passage of overcurrent through it.
- Disconnector: A Switch that is a manually operated or motor operated mechanical switching device used for changing the connections in a circuit, or for isolating a circuit or equipment from a source of power.
- Jumper: A short section of conductor with negligible impedance which can be manually removed and replaced if the circuit is de-energized.
- Conductor: A combination of conducting material with consistent electrical characteristics, building a single electrical system, used to carry current between points in the power system.
- ACLineSegment: A wire or combination of wires, with consistent electrical characteristics, building a single electrical system, used to carry alternating current between points in the power system.
- PowerTransformer: An electrical device consisting of two or more coupled windings, with or without a magnetic core, for introducing mutual coupling between electric circuits.
- TransformerWinding: A winding is associated with each defined terminal of a transformer.
- TapChanger: A mechanism for changing transformer winding tap positions.
- RatioTapChanger: A tap changer that changes the voltage ratio impacting the voltage magnitude but not direclty the phase angle across the transformer.
- WindingTest: Physical winding test data for the winding/tap pairs of a transformer. This test data can be used to derive other attributes of specific transformer or phase shifter models.
- ShuntCompensator: A shunt capacitor or reactor or switchable bank of shunt capacitors or reactors. ShuntCompensator is a single terminal device.
- SynchronousMachine: An electromechanical device that operates synchronously with the network. It is a single machine operating either as a generator or synchronous condenser or pump.
- FaultIndicator: An indicator (which may or may not be remotely monitored) that assists with determining circuit section where a fault most likely happened.
- EnergyConsumer: A generic user of energy -- a point of consumption on the power system model.


