For the field unit, the backdrop geodatabase is a personal or file geodatabase that provides a "snapshot" of the data as it exists on the enterprise geodatabase. The backdrop does not have to contain all the features in your Enterprise geodatabase, but rather would be a subset that includes only the features necessary to field users. For example, the data may be subdivided into service areas in which each field user works. Reducing the number of tables and feature classes in the backdrop to only the necessary minimum improves performance.
 |
Mobile does not support any relationship involving a non-ArcFM (or non-Designer) object in the Backdrop database.
|
The following steps describe how to create your backdrop geodatabase. Use Geodatabase Replication (discussed later) to maintain the backdrop geodatabase.
 |
To view Feeder Manager 2.0 data in the geodatabase backdrop, after creating the backdrop, ensure you have Feeder Manager 2.0 enabled in ArcCatalog. |
File Geodatabases: If you wish to use a file geodatabase in the field, note that this database cannot be compressed because the field user is editing it directly. Geodatabase Replication offers some options:
- Don't compress the file geodatabase on the server. An uncompressed file geodatabase is larger and can take longer to download to the client, but additional time is NOT required to uncompress on the client.
- Compress on the server and uncompress on the client. The compressed file geodatabase will take less time to download to the client and use less bandwidth. However, additional time is required to uncompress the file geodatabase once it's on the client machine.
Access Geodatabase: Although the Access database size limit is 2GB, ESRI recommends limiting your Access database size to 500MB or less to ensure effective performance and stability.
Create Initial Extract Version and Initial Extract Geodatabase
- In ArcCatalog, you'll need to create the Initial Extract version from which the data will be extracted. This version will likely be created on your Enterprise database. Add the Versions command to a toolbar:
- From the Customize menu, select Customize Mode.
- In the Commands tab, click Database connection in the Categories list.
- Click Versions in the Commands list and drag it to a toolbar. Close the Customize window.
- Login (Connect) to an enterprise geodatabase and click the Versions tool you just added to the toolbar. The Geodatabase Administration window opens. In the Versions tab, select the DEFAULT version, right-click it and select New Version.
- On the New Version screen, enter the name of your Initial Extract version (any name) and ensure it is private. Click OK.
- Create an Initial Extract version for each replica. When you've finished, close the Version Manager.
- Right-click the geodatabase in ArcCatalog and select Disconnect. Close and restart ArcCatalog.
In the next steps, you will execute several ArcFM Solution tools in ArcCatalog.
- On your Administrator machine, right-click a folder in ArcCatalog and select New to create an empty file geodatabase (*.gdb) or personal geodatabase (*.mdb). This will become your backdrop geodatabase.
 |
Mobile users: The Backdrop geodatabase is created on the Administrator machine because the directory structure on your Administrator machine is exactly the same as the directory structure on your field machines. In a later step, you will connect stored display layers from the Login database to the Backdrop geodatabase. It is critical that these databases reside in the exact directory structure used in the field when these layers are connected. This ensures the stored display layers will remain connected for field users after the databases are distributed by Geodatabase Replication.
|
- Right-click your newly created (empty) personal or file geodatabase and execute the Create/Update ArcFM Solution System Tables tool. This creates the necessary ArcFM system tables in your new geodatabase.
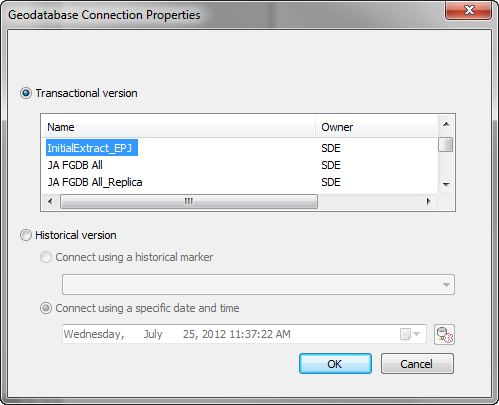
- Connect to the Initial Extract version you created in earlier steps. Right-click your Enterprise geodatabase and select Geodatabase Connection Properties. Ensure that the Transactional radio button is checked and select the initial extract version you created. This will cause ArcCatalog to use this version when connecting. You must connect to the Initial Extract version. If you accidentally connect to the SDE.Default version before copying data to your new database, you will lose changes in future backdrop updates.
- Copy and paste data from the Initial Extract version(s) in SDE into the personal or file geodatabase created in earlier steps. If you require a spatial subset, try using ESRI's Create Replica tool (see ArcGIS online help for more information). This copy or extract MUST come from the Initial Extract version(s). Note that if you copy the Landbase dataset, you will need a Network Analyst extension license.
- Close ArcCatalog and restart it.
- Run the Upgrade ArcFM Solution Database tool on your new personal or file geodatabase. This tool updates your geodatabase with modifications required by the latest release.
- Next, select your SDE geodatabase (Enterprise) and run ArcFM XML Export. Select all export options. This tool exports the selected information (export options) to an XML file.

- Select the personal or file geodatabase you created earlier and use the ArcFM XML Import tool to import the data from the previous step. This imports data such as model name assignments, ArcFM properties, snapping information, etc.
If you do not use Mobile, continue to step 16. Mobile users only: Assign the MM Field Edit model name to the geodatabase. The MM Field Edit model name is necessary if you have a stored display that points to multiple workspaces (i.e., databases). When the field user opens the stored display that points to multiple databases, the layers will point to the database that has this model name assigned.
- Right-click the geodatabase and select ArcFM Properties Manager.
- On the Model Names tab, select the Domain Independent Database Model Name domain.
- Select MM FIELD EDIT in the Model Names Available field and double-click it to move it to the Model Names Selected field. Remove the MM ENTERPRISE model name from the Model Names Selected field.
- Disable any virus-scanning software. If you use Microsoft Security Essentials, for example, follow these steps to temporarily disable real-time protection:
- Open Microsoft Security Essentials.
- Click the Settings tab.
- Click Real-time protection in the left pane.
- Uncheck Turn on real-time protection.
- Click Save Changes.
- Run the ArcFM Set ServerOIDs tool on your new geodatabase. You may need to add this command via the Customize menu. This tool populates the ServerOID field with the appropriate values. The time required to run this tool varies according to the size and complexity of your database. Learn more about this tool in the help topic titled ArcFM Set Server OIDs.
- Re-enable real-time protection in Microsoft Security Essentials, or re-enable your other virus-scanning software.
- Place the backdrop database on the Administrator or client machine in the location where users will access it. The database must be in its permanent location before connecting the layers in the next step. You can copy the backdrop database to another machine after connecting the layers, but it must be placed in the same path to prevent breaking the data sources. Field users will most likely not have the ability to connect broken data sources. If you do change the path of the backdrop database, be sure to run the ArcFM Data Source Wizard to fix broken data sources.
 |
Geodatabase Replication: The location of the backdrop database may depend on the base path and client base path set up for Geodatabase Replication. Now is a good time to review the instructions for creating the base path on the server and the client base path to ensure your backdrop database is properly located for replication. If you move your backdrop database to the Server Base Path, be sure to run the ArcFM Data Source Wizard once the backdrop database is in the correct location for Geodatabase Replication.
|
Open the Backdrop database in ArcMap and connect any broken data sources. Create any stored displays to be used by field users. Field users will most likely not have the ability to connect broken data sources or create stored displays.
 |
Geodatabase Replication: The backdrop should be kept as current as possible. If you have a regular posting/reconcile process in place, the backdrop would ideally be refreshed with each iteration of that process. The Geodatabase Replication tool is used to refresh the backdrop. If you wish to configure Geodatabase Replication to maintain this database, copy the Backdrop database you just created to the Initial Extracts folder in the Geodatabase Replication Base Path on the Replication Server.
Autoupdaters: When features are imported from the field to the enterprise, all edits that were performed in the field are duplicated (or replayed) on the Enterprise. However, autoupdaters are not executed (unless configured, see below) while importing field edits to the Enterprise. All necessary autoupdaters must fire when the edits are made in the field.
There may be an instance where an autoupdater exists on the Enterprise, but not in the field. You can configure an autoupdater like this to fire when the mobile edits are replayed on the Enterprise machine during import. Use the On Mobile Feature Create, On Mobile Feature Update, and On Mobile Feature Delete feature properties in the ArcFM Properties Manager (Object Info tab) to specify the autoupdater(s) that should fire on the Enterprise while replaying edits from the field.
|
Add Stored Displays to the Backdrop
These steps are necessary only if you are NOT using a login database.
Follow these steps to copy stored displays from the Enterprise database into the backdrop. If you're using a login database, skip the following set of steps and go to the Configure Backdrop for ArcFM Solution section instead.
 |
If you are using Feeder Manager 2.0, re-save your stored displays on the Enterprise database prior the steps below. |
- In the backdrop database, delete the MM_SYSTEM_STORED_DISPLAYS and MM_SYSTEM_PACKAGES tables.
- In ArcCatalog, copy MM_SYSTEM_STORED_DISPLAYS and MM_SYSTEM_PACKAGES from your Enterprise database and paste them into the backdrop database. This adds all system stored displays in the Enterprise to the Backdrop.
- Select the Backdrop database and click the Data Source Wizard
 button on the ArcFM Solution toolbar in ArcCatalog. In the next few steps you will use this tool to connect the stored display layers to the feature layers in the backdrop geodatabase.
button on the ArcFM Solution toolbar in ArcCatalog. In the next few steps you will use this tool to connect the stored display layers to the feature layers in the backdrop geodatabase.
- Read the information provided on the first screen and click Next.
- Select the stored display(s) and/or document(s) you'd like the mobile user to access in the field. All unnecessary stored displays and documents will be removed later. Click Next.
- You will need to set all data sources, so accept the default setting on the next screen. Click Next.
- Browse to the Backdrop geodatabase (same database in which the stored displays now reside) when selecting the destination data source. This connects the layers in the selected stored displays/documents to the backdrop. Click Next.
- Review the Summary and click Next to connect the stored display/document layers to the Backdrop geodatabase.
- Next, open the backdrop database in ArcMap and delete any stored displays and/or documents that the user will not require in the field. This will likely include all stored displays you chose not to connect using the Data Source Wizard.
Add CUs and Favorites for Designer
These steps are only necessary for those who use Mobile Designer.
Perform the following steps on your initial extract (backdrop) database.
- In ArcCatalog, select the backdrop database and open the CU Administration tool. Click Execute on the Update Schema tab. This creates the following tables.
- MM_CU_ATTRIBUTES
- MM_CU_DOMAINFILTER
- MM_CU_EXTENDED_DATA
- MM_CU_LIBRARY
- MM_CU_SEARCH_XML
- MM_CU_SYS_PALETTES_XML
- Close the CU Administration tool.
- Restart ArcCatalog.
- In ArcCatalog, login to the Enterprise database and open the System Favorites Manager.
- On the Compatible Units tab, export the Compatible Units and (optionally) the System Favorites you wish to make available in the field.
- Click Export. Give the exported XML file a name and click Save. If you're exporting both CU and favorites, you will have multiple exported XML files.
- Click OK to dismiss the System Favorites Manager.
- Select the Backdrop database and open the System Favorites Manager.
- On the Compatible Units tab, expand the Compatible Units node and delete all CUs. In the System Favorites list, delete any favorites you intend to import. If you don't delete the existing CUs and system favorites, you'll have duplicates after importing in the next step.
- Select the node that corresponds to the XML you're importing (i.e., select Compatible Units node to import CUs) and import the XML you exported in previous steps.
- Click OK to dismiss the System Favorites Manager.
- Select the backdrop database and open the CU Administration tool.
- Select the Migrate Data tab and click the Upgrade Compatible Units button.
- Close the CU Administration tool.
Feature-Linked Annotation Layers
If you have feature-linked annotation layers, remove the Auto-Create ESRI property on your backdrop geodatabase. Otherwise, you will end up with duplicates when doing mobile transport.
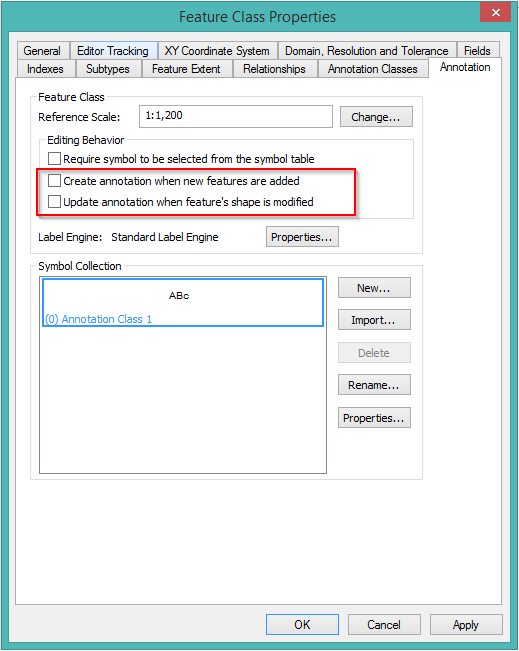
- In ArcCatalog, right-click the feature and select Properties.
- Select the Annotation tab.
- Ensure that Create annotation when new features are added and Update annotation when feature's shape is modified are unchecked.
- Click OK.








 button on the ArcFM Solution toolbar in ArcCatalog. In the next few steps you will use this tool to connect the stored display layers to the feature layers in the backdrop geodatabase.
button on the ArcFM Solution toolbar in ArcCatalog. In the next few steps you will use this tool to connect the stored display layers to the feature layers in the backdrop geodatabase.